- Phone:+86-17331948172 +86-0319-8862898
- E-mail: inquiry@puxingclamp.com
aug . 23, 2025 02:20 Back to list
Premium 201 Stainless Steel Strip - Durable & Cost-Effective
Understanding 201 Stainless Steel Strip in B2B Applications
In the demanding landscape of modern manufacturing and industrial infrastructure, material selection is paramount. Among the diverse grades of stainless steel, the 201 stainless steel strip emerges as a highly sought-after material, particularly where a balance of cost-effectiveness, adequate corrosion resistance, and excellent formability is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the technical intricacies, application versatility, and market dynamics surrounding this essential industrial commodity, providing B2B decision-makers with the insights needed for optimal procurement and utilization.
The robust characteristics of 201 stainless steel strip make it a preferred choice across numerous sectors, including kitchenware, automotive components, architectural trim, and various consumer goods. Its unique chromium-nickel-manganese composition offers properties distinct from its counterparts, such as 304 and 316 grades, positioning it as a strategic alternative in many engineering contexts.
Detailed Manufacturing Process Flow of 201 Stainless Steel Strip
The production of 201 stainless steel strip is a complex, multi-stage process that ensures the material meets stringent industry standards for metallurgical integrity and mechanical performance. Starting from raw alloy constituents to the final precision-slit coils, each step is meticulously controlled to achieve the desired properties.
Key Stages in Production:
1. Melting and Casting
Raw materials, including iron ore, nickel, chromium, and manganese, are melted in an electric arc furnace (EAF) to form a molten stainless steel alloy. This molten metal is then refined in an argon oxygen decarburization (AOD) converter to achieve the precise chemical composition of 201 stainless steel strip. Subsequently, it is continuously cast into slabs or blooms.
2. Hot Rolling
The cast slabs are reheated and then passed through a series of rollers at high temperatures (above recrystallization temperature). This process reduces the thickness of the material significantly, forming hot-rolled coils or plates, while refining the grain structure.
3. Annealing and Pickling
Hot-rolled coils undergo annealing—a heat treatment process involving heating to a specific temperature and then controlled cooling—to relieve internal stresses, improve ductility, and soften the material. After annealing, pickling removes the scale and impurities from the surface, typically using acid baths, to prepare for cold rolling.
4. Cold Rolling
The annealed and pickled material is then cold-rolled at room temperature, which further reduces its thickness, enhances surface finish, improves dimensional accuracy, and increases its strength and hardness. Multiple passes through cold rolling mills are often required to achieve the final gauge.
5. Finishing and Slitting
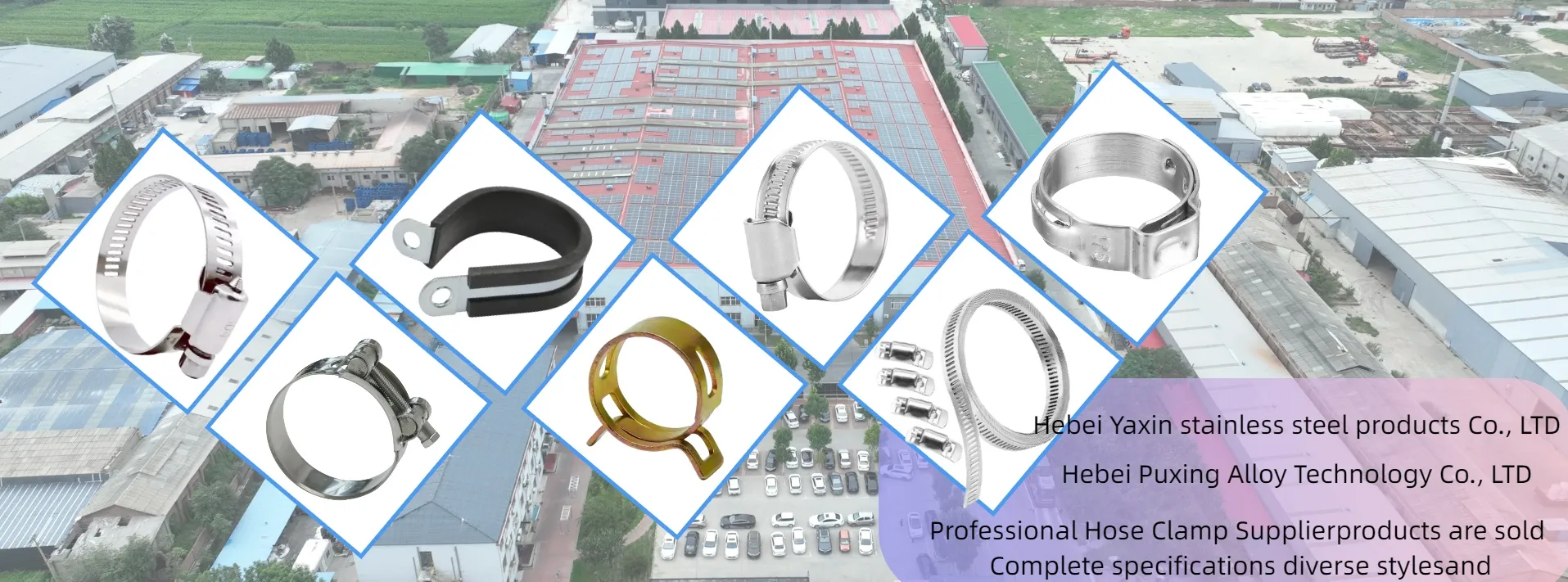
After cold rolling, the material may undergo additional annealing and pickling, along with various finishing processes such as skin passing (light cold rolling for surface quality) or polishing to achieve specific surface finishes (e.g., BA, 2B, NO.4). Finally, the wide coils are precisely slit into narrower stainless steel strip coil according to customer specifications, and then packaged for shipment.
Throughout these stages, rigorous testing standards are applied. Our products conform to international benchmarks such as ISO 9001 for quality management and relevant ASTM/ANSI standards for material composition and mechanical properties. This ensures a consistent service life and optimal performance in target industries, including petrochemical, metallurgy, water supply & drainage, and automotive manufacturing. The inherent advantages, such as energy saving during fabrication due to its formability and its adequate corrosion resistance for general applications, are maintained through strict process control.

Figure 1: Illustration of a cold rolling mill for stainless steel strip production.
Industry Trends and Market Dynamics of Stainless Steel Strip
The global market for stainless steel strip is constantly evolving, driven by economic growth, technological advancements, and shifting material demands across various industrial sectors. The demand for 201 stainless steel strip, alongside 304 stainless steel strip and 316 stainless steel strip, reflects broader trends in infrastructure development, consumer goods, and industrial equipment manufacturing.
Recent market analysis indicates a steady growth trajectory for stainless steel, fueled by increased urbanization and industrialization, particularly in emerging economies. The versatility of stainless steel strip coil products, offering a balance of strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance, ensures their continued relevance. Furthermore, the emphasis on sustainability is prompting innovations in production processes, aiming for reduced environmental impact and enhanced recyclability.
The role of `china stainless steel strip` manufacturers in meeting global demand cannot be overstated. With significant production capacities and continuous investment in advanced manufacturing technologies, Chinese suppliers play a pivotal role in the supply chain, offering competitive pricing and diverse product portfolios, including various grades and finishes of 201 stainless steel strip. This global dynamic fosters a competitive environment, benefiting end-users through wider material choices and optimized costs.

Figure 2: Global stainless steel market demand trends.
Technical Specifications of 201 Stainless Steel Strip
Understanding the precise technical specifications of 201 stainless steel strip is crucial for engineers and procurement specialists. This austenitic stainless steel grade is characterized by its lower nickel content compared to 304, with manganese and nitrogen partially replacing nickel, leading to distinct mechanical properties and cost advantages.
Chemical Composition (Typical Weight %):
| Element | Min (%) | Max (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | - | 0.15 |
| Silicon (Si) | - | 1.00 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 5.50 | 7.50 |
| Phosphorus (P) | - | 0.060 |
| Sulfur (S) | - | 0.030 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 16.00 | 18.00 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 3.50 | 5.50 |
| Nitrogen (N) | - | 0.25 |
Mechanical Properties (Typical, Annealed Condition):
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (UTS) | 515 (min) | MPa |
| Yield Strength (0.2% Offset) | 275 (min) | MPa |
| Elongation (% in 50mm) | 40 (min) | % |
| Hardness (Rockwell B) | 95 (max) | HRB |
These properties indicate that 201 stainless steel strip offers good strength and formability, making it suitable for drawing and forming operations. Its cold work hardening rate is comparable to that of 304 stainless steel, which can be advantageous in applications requiring increased strength after cold forming.
Figure 3: Precision-slit stainless steel coils ready for distribution.
Application Scenarios of 201 Stainless Steel Strip
The versatility of 201 stainless steel strip positions it as a material of choice across a spectrum of industrial and commercial applications. Its balanced properties, including moderate corrosion resistance and excellent cold formability, make it an attractive option where cost-effectiveness is a key consideration without significant compromise on performance.
- Kitchenware and Appliances: Due to its pleasing aesthetic and good formability, 201 stainless steel strip is widely utilized in the manufacturing of sinks, cooking utensils, serving dishes, and components for domestic appliances like washing machines and refrigerators. It provides a durable, easy-to-clean surface that resists tarnishing in typical indoor environments.
- Automotive Industry: Components such as trim, decorative elements, and some structural parts where high corrosion resistance is not paramount but strength and formability are required. Its use contributes to weight reduction and enhanced aesthetics.
- Architectural and Decorative Applications: Interior architectural trim, door frames, window components, and shop fittings often benefit from the appearance and workability of 201 stainless steel strip. It offers a cost-effective alternative to 304 in less aggressive environments.
- Industrial Equipment and Components: Used in various non-critical parts of industrial machinery, tanks, and enclosures, particularly where the material is not exposed to harsh chemical or marine environments. Its strength-to-weight ratio is advantageous in many structural roles.
- Railway Cars and Trailers: For specific internal and external components of transportation vehicles, especially where moderate strength and good formability are needed, 201 grade offers a robust solution.
Customer feedback consistently highlights the superior formability and aesthetic finish achievable with 201 stainless steel strip, making it a reliable choice for high-volume production of intricate components. Its ability to undergo deep drawing and bending without significant work-hardening issues translates into energy saving during fabrication and reduced tooling wear, ultimately lowering production costs.
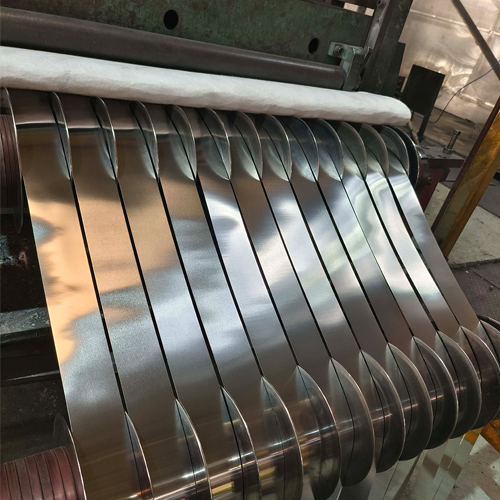

Figure 4: A common application of stainless steel in kitchenware manufacturing.
Technical Advantages of 201 Stainless Steel Strip
Choosing the right stainless steel grade involves a careful evaluation of its technical advantages relative to specific application demands. While 201 stainless steel strip may not offer the same level of corrosion resistance as grades like 304 or 316, it presents compelling benefits in certain contexts, particularly concerning cost-efficiency and mechanical properties.
- Cost-Effectiveness: A primary advantage of 201 stainless steel strip stems from its chemical composition. By replacing a significant portion of costly nickel with manganese and nitrogen, it offers a more economical solution without drastically compromising essential properties. This makes it an attractive choice for high-volume production and projects with budget constraints.
- High Strength and Hardness: The nitrogen content in 201 grade contributes to a higher tensile strength and yield strength compared to 304, particularly in the cold-rolled condition. This property is beneficial in applications requiring robust structural integrity and resistance to deformation, allowing for potentially thinner gauges and material savings.
- Excellent Formability: Despite its higher strength, 201 stainless steel strip exhibits good ductility and formability, making it suitable for various fabrication processes such as deep drawing, bending, and roll forming. This ease of processing translates into lower manufacturing costs and greater design flexibility.
- Moderate Corrosion Resistance: While not designed for harsh corrosive environments, 201 offers adequate corrosion resistance for many indoor and mild atmospheric applications. Its chromium content ensures the formation of a passive layer that protects against rust and staining under normal conditions, contributing to a satisfactory service life.
Comparative Analysis: 201 vs. 304 vs. 316 Stainless Steel Strip
To fully appreciate the benefits of 201 stainless steel strip, it's essential to compare it with other common austenitic grades.
| Feature | 201 Stainless Steel Strip | 304 Stainless Steel Strip | 316 Stainless Steel Strip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Alloying Elements | Cr-Mn-Ni-N | Cr-Ni | Cr-Ni-Mo |
| Cost-Effectiveness | High (most economical) | Medium | Low (most expensive due to Mo) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (suitable for mild environments) | Good (general purpose) | Excellent (superior pitting/crevice resistance, ideal for marine/chemical) |
| Tensile Strength (Annealed) | High (e.g., 515-725 MPa) | Medium (e.g., 515-690 MPa) | Medium (e.g., 515-690 MPa) |
| Formability | Good | Excellent | Good |
| Weldability | Fair (requires careful parameter control) | Excellent | Very Good |
This comparison highlights that while 304 and 316 offer superior corrosion resistance, particularly in aggressive environments due to their higher nickel and molybdenum content respectively, 201 stainless steel strip presents a viable and economically attractive alternative for applications where its moderate corrosion resistance and higher strength are sufficient.
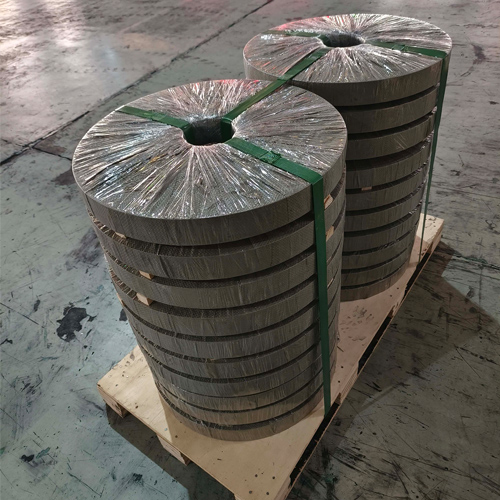

Figure 5: Different gauges and widths of stainless steel strip coils.
Vendor Comparison and Selection for Stainless Steel Strip
Selecting the right supplier for stainless steel strip coil, including specific grades like 201 stainless steel strip, is a critical decision for B2B enterprises. A reliable vendor ensures consistent product quality, competitive pricing, and robust logistical support.
Key Factors in Vendor Evaluation:
- Quality Certifications: Ensure the vendor adheres to international quality management systems like ISO 9001 and that products meet relevant ASTM, EN, or JIS standards. Request test data and material certificates (MTCs) for each batch.
- Production Capacity and Lead Times: Evaluate the supplier's ability to meet your volume requirements and deliver within acceptable lead times. For example, reputable `china stainless steel strip` manufacturers often possess large-scale facilities capable of high-volume output.
- Customization Capabilities: Assess their flexibility in providing tailored dimensions, specific finishes (e.g., 2B, BA, No.4, HL), and specialized mechanical properties.
- Technical Support and After-Sales Service: A strong vendor provides expert technical assistance, from material selection guidance to troubleshooting, and offers reliable after-sales support.
- Experience and Reputation: Look for vendors with a proven track record, extensive years of service in the industry, and positive client testimonials or partner clients from respected sectors.
Our company, for instance, has proudly served the global market for over a decade, supplying premium 201 stainless steel strip and other grades to leading manufacturers in the automotive, construction, and household appliance sectors. Our commitment to ISO 9001 certified processes and comprehensive test data ensures product reliability and customer satisfaction.
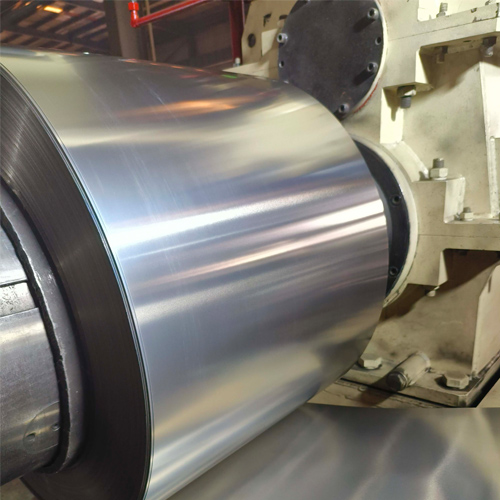

Figure 6: A quality control inspection of stainless steel strip.
Customized Solutions for 201 Stainless Steel Strip
Recognizing that standard product offerings may not always suffice for unique engineering challenges, we specialize in providing customized solutions for 201 stainless steel strip. Our capabilities extend beyond conventional specifications to meet the precise demands of complex projects.
Tailored Customization Options:
- Precision Slitting: We offer slitting services to achieve specific widths from wide coils, ranging from narrow strips for intricate components to broader sections for structural elements, with precise tolerances.
- Gauge Optimization: Custom thickness requirements can be met through specialized cold rolling processes, optimizing material usage and mechanical performance for specific applications.
- Surface Finishes: A range of surface finishes (e.g., dull, bright annealed, brushed, mirror) can be applied to enhance aesthetic appeal or improve functional properties like cleanability and corrosion resistance for the stainless steel strip coil.
- Specialized Mechanical Properties: Through controlled annealing and temper rolling, we can adjust the hardness and ductility of the 201 stainless steel strip to suit specific forming or stamping operations, ensuring optimal yield and reduced scrap.
- Protective Packaging: Custom packaging solutions, including interleaving paper, protective films, and robust crating, are available to ensure the material arrives in pristine condition, ready for immediate processing.
Our engineering team collaborates closely with clients from conceptualization through to production, ensuring that every customized 201 stainless steel strip solution precisely aligns with project requirements and performance expectations.

Figure 7: A selection of stainless steel strips with various finishes.
Application Case Studies: 201 Stainless Steel Strip in Action
Real-world applications best illustrate the practical advantages and performance capabilities of 201 stainless steel strip. These case studies demonstrate how our materials provide effective solutions for diverse industrial needs.
Case Study 1: Automotive Trim Components
A leading automotive manufacturer sought a cost-effective material for exterior decorative trim and interior panel accents. The primary requirements were good formability for intricate shapes, a bright aesthetic finish, and sufficient corrosion resistance against typical road conditions (e.g., light exposure to salt, moisture).
- Challenge: Reduce material costs while maintaining a premium look and acceptable durability.
- Solution: We supplied precision-slit 201 stainless steel strip with a BA (Bright Annealed) finish. Its excellent ductility allowed for complex stamping operations, and its inherent brightness provided the desired aesthetic without extensive post-processing.
- Outcome: The manufacturer achieved a 15% reduction in material costs compared to 304 stainless steel, with no compromise on visual quality or performance in the specified application environment. Accelerated corrosion tests confirmed adequate resistance.
Case Study 2: Commercial Kitchen Equipment Fabrication
A fabricator of commercial kitchen counters and shelving needed a material that was easy to weld and form, offered good hygiene properties, and was resistant to general food acids and frequent cleaning, all while remaining budget-friendly.
- Challenge: Find a cost-effective material with good workability and surface hygiene for non-critical, interior kitchen environments.
- Solution: We provided 201 stainless steel strip in wider coils with a 2B finish, ideal for surface flatness and moderate reflectivity. Its excellent formability facilitated efficient bending and welding for large panel fabrication.
- Outcome: The project saw a significant reduction in fabrication time due to the material's workability. The finished equipment demonstrated excellent service life in typical commercial kitchen settings, validating 201's suitability for such applications where direct contact with aggressive chemicals is limited.

Figure 8: Stainless steel components in a finished industrial product.
Trust and Reliability: FAQ, Lead Time, Warranty, and Support
Building strong B2B partnerships is founded on transparency, clear communication, and unwavering support. We are committed to ensuring our clients have all the information and assistance they need from inquiry to post-delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the primary differences between 201, 304, and 316 stainless steel strip?
A: The main difference lies in their chemical composition, particularly nickel and molybdenum content. 201 stainless steel strip has lower nickel and higher manganese/nitrogen, making it more cost-effective and harder but with slightly reduced corrosion resistance compared to 304. 316 contains molybdenum, offering superior resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, ideal for marine or chemical environments.
Q: Can 201 stainless steel strip be welded?
A: Yes, 201 can be welded using standard methods, though it may require careful attention to welding parameters and filler metal selection to avoid sensitization and intergranular corrosion, especially in thicker sections. Low carbon filler metals are often recommended.
Q: What surface finishes are available for 201 stainless steel strip?
A: We offer a variety of finishes, including 2B (smooth, moderately reflective), BA (bright annealed, highly reflective), No.4 (brushed finish), and customized options to meet specific aesthetic or functional requirements.
Q: How do you ensure the quality of your stainless steel strip products?
A: Our manufacturing processes are ISO 9001 certified. We implement rigorous quality control at every stage, from raw material inspection to final product testing. Each batch is supplied with a Material Test Certificate (MTC) detailing its chemical composition and mechanical properties, confirming compliance with international standards.
Lead Time & Fulfillment
Standard orders for common dimensions of stainless steel strip coil typically have a lead time of 2-4 weeks. For customized specifications or large-volume orders, lead times may vary and will be communicated clearly during the quotation process. We employ efficient logistics partners to ensure timely and secure delivery globally, accommodating various shipping terms (FOB, CIF, DDP). Expedited options are available upon request for urgent projects.
Warranty Commitments
All our 201 stainless steel strip products are backed by a comprehensive warranty against manufacturing defects and non-compliance with agreed-upon specifications. We guarantee that materials will meet the chemical composition and mechanical properties outlined in their respective Material Test Certificates. Specific warranty periods and conditions are detailed in our sales agreements and are designed to provide our clients with complete peace of mind.
Dedicated Customer Support
Our dedicated customer support team is available to assist with all inquiries, from technical specifications and product selection to order tracking and after-sales service. We offer multi-channel support via phone, email, and a dedicated online portal. Our engineers are available for technical consultations to help you optimize material usage and troubleshoot any application-specific challenges. We pride ourselves on responsive and knowledgeable assistance, ensuring a seamless experience for our B2B partners.
References
- ASM International. (2002). ASM Handbook, Volume 1: Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys. ASM International.
- Outokumpu. (Year not specified). Handbook of Stainless Steel. Outokumpu.
- International Stainless Steel Forum (ISSF). (Latest Annual Report). Stainless Steel in Figures. International Stainless Steel Forum.
- ASTM International. (Latest Standards). ASTM A666/A666M - 15 Standard Specification for Annealed or Cold-Worked Austenitic Stainless Steel Sheet, Strip, Plate, and Flat Bar. ASTM International.
- Euro Inox. (Year not specified). Stainless Steel Reference Manual. Euro Inox.
This is the last article
-
Premium 201 Stainless Steel Strip - Durable & Cost-Effective
NewsAug.23,2025
-
Precision High Quality Stainless Steel Strip Coils & Rolls
NewsAug.22,2025
-
Durable Adjustable Hose Clamps for Pipes & Radiators
NewsAug.21,2025
-
Heavy Duty Hose Clamps: Premium Stainless Steel & Adjustable
NewsAug.19,2025
-
Large Stainless Steel Adjustable American Type Hose Clamp - Hebei Pux Alloy Technology Co., Ltd
NewsAug.18,2025
-
Large Stainless Steel Adjustable Hose Clamp - Hebei Pux Alloy|Durable Corrosion Resistance&Adjustable Design
NewsAug.18,2025




